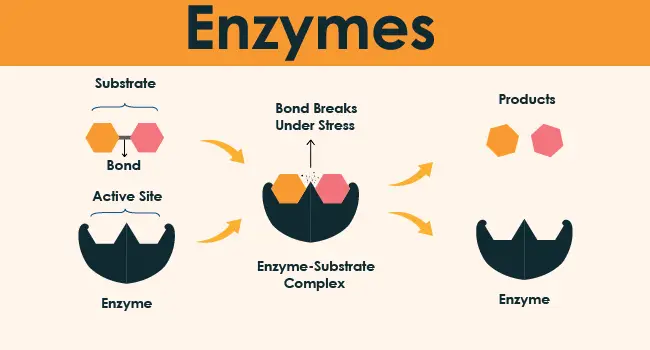
What are Enzymes ?
What are enzymes: These are a class of molecules of biological catalysts. They can accelerate the speed of chemical reactions. At a point when one substance should be changed into another, nature utilizes proteins to accelerate the procedure. A reaction catalyzed by an enzyme is called an “enzymatic” reaction.
Different people have different ways of thinking about enzymes. I want you to know correctly without getting You into confusion.
These are actually biological macromolecules with a molecular mass of at least 10,000, and large ones can reach one million. They are a very important type of biocatalyst. Due to the action of which, chemical reactions in organisms can proceed efficiently and specifically under extremely mild conditions.
What are Enzymes Made of?
What are Enzymes Made of: Enzyme are made of proteins, and structural components of these are amino acids. All the protein elements of our body are made up of 20 basic amino acids. These amino acids are joined together in a long chain that determines the three-dimensional structure of an enzyme.
Factors Affecting Enzymes Activity
Factors Affecting Enzymes Activity: The factors that most directly influence the activity of an enzyme are:
- pH
- temperature
- cofactor
Classification and Examples Of Enzymes
Examples Of Enzymes: Everything that ends in –ase is an enzyme. For example: lactase that breaks down lactose into its two simple sugars: glucose and galactose, lipase transforms lipids (triacylglycerol into glycerol), etc. Ptyaline in saliva or pepsin in the stomach are also enzymes, although they do not end in -ase.
Enzyme Classifications as follows;
- Transferases. They transfer functional groups (such as methyl or phosphate groups), such as methyltransferase, aminotransferase, hexokinase, phosphorylase, etc.
- Ligases. These catalyze specific substrate-binding reactions, by simultaneous hydrolysis of triphosphate nucleotides (such as ATP or GTP).
- Liasas. Enzymes that catalyze the breakdown or welding of substrates. For example, acetate decarboxylase.
- Oxidoreductases. They catalyze oxide-reduction reactions, that is, transfer of electrons or hydrogen atoms from one substrate to another. An example of these are the enzymes dehydrogenase and c oxidase.
- Hydrolases. They deal with hydrolysis reactions (the breakdown of organic molecules by water molecules). For example, lactase.
- Isomerases. They catalyze the interconversion of isomers, that is, they convert a molecule into its three-dimensional geometric variant.
Functions and Uses
Functions of Enzymes: Without vitamins many enzymes can’t function properly causing metabolic disturbances. They play an important role in our immune system, regulating inflammatory processes & blood flow. They have functions such as digestion, absorption, decomposition, excretion of food, promotion of metabolism.
Uses Of Enzymes: These are of great importance and are used in virtually all areas of life.
- In the leather industry, they soften the skin.
- Amylase, protease, lipase are actively used in medicine.
- Used for the manufacture of sausages, canned goods, cheeses and smoked meats.
- They are used for the processing of crops and the preparation of feed.
- They are involved in a huge number of chemical processes in various industrial fields.
you may also enjoy: