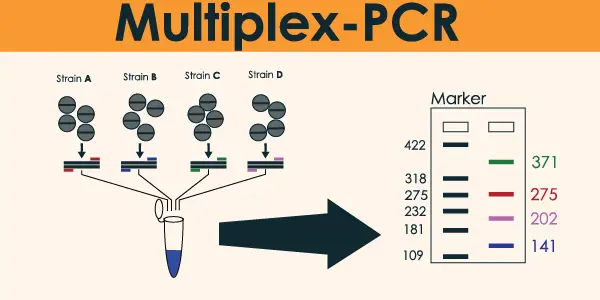
What is Multiplex PCR
Multiplex PCR OR PCR multiplexing also known as multiple primer PCR or simply DNA multiplexing, is a modified version of the polymerase chain reaction used to detect deletions and duplications in large genes. The process is the same as general PCR. It is suitable for saving experiment time because different single PCRs are performed in a single reaction.
Genetic products can be compared under the same amplification conditions. Due to these advantages, Multiplex type of PCR can be used for diagnostic PCR, such as processing large samples or detecting multiple similar species and can also be used to simultaneously compare the expression of several genetic products.
For multiplex PCR to be successful, enough endpoints must be generated by an endpoint detection method such as gel electrophoresis to detect all sequences of interest. This type of PCR is used to obtain qualitative results. We used Real-time PCR multiplex for qualitative or quantitative results.
Multiplex PCR Test and its importance.
It Is simply efficient, systematic, and economical. The biggest value of this type of PCR technology is that it can improve the sensitivity of diagnosis. Sensitivity can be analyzed in two ways: Analytical Sensitivity and Clinical Sensitivity.
The expression “plex” is used to describe multiplets. Singleplex is an assay designed to amplify a single gene sequence. Duplex is an assay designed to amplify the sequence of two genes. Duplex is the most common multiplex, in which the target gene is assayed in the same well as the control or standardized gene.
I guess you are interested to gain more knowledge about this type of PCR. Come go more in detail.
Characteristics:
The characteristics of multiple PCR are:
- High efficiency: Multiple pathogenic microorganisms can be detected in the same PCR reaction tube at the same time, or target genes with multiple types can be typed, especially with a drop of blood to detect multiple pathogens.
- Systematic: Multiplex PCR is very suitable for the detection of groups of pathogens, such as the hepatitis virus, intestinal pathogenic bacteria, sexually transmitted diseases, non-spore anaerobic bacteria, war wound infection bacteria and bacterial warfare agents.
- Economic simplicity: Multiple pathogens are detected in the same reaction tube at the same time, which will greatly save time, save reagents, save money, and provide more and more accurate diagnostic information for clinical.
Advantages of Multiplex PCR
- Three advantages of multiplex PCR increased throughput (available many samples than per plate assay), reduction of the sample amount and decrease the usage amount of the reagent is.
- Another advantage of multiplexing with targets and endogenous controls is the ability to minimize pipetting errors.
- The benefits of multiplex accuracy are especially important for quantitative experiments that require higher accuracy.
Applications of Multiplex PCR
Applications for multiplex PCR include:
- High throughput SNP Genotyping (TaqMan)
- Identification of causative bacteria and viruses in infectious diseases
- High throughput STR Genotyping
- Mutation analysis
- Pathogen identification
- Template quantification
- Gene expression analysis
- RNA detection
- Obesity research
- Linkage analysis
- Forensic research
Limitations of Multiplex PCR
- Blending various primers can cause some obstruction in the intensification interaction, particularly as the quantity of various primers sets utilized increments.
- Sequencing of enormous successive genomic areas by multiplex PCR can make a cross-response between preliminary matches because of overlaps of primers.
Commercial Application of Multiplex PCR
- E-sensor innovation from GenMark Diagnostics also takes in consideration of multiplex PCR as well as RT-PCR to enhance an assortment of nucleic corrosive targets.
- Biofire Film-array technique of bioMerieux utilizes a settled blend of, multiplex, nested and traditional PCR responses to recognize an assortment of microorganisms.
Conclusion:
It is a PCR method category in which more than one objective grouping is enhanced utilizing various arrangements of primers inside a solitary PCR blend. This empowers intensification of a few quality fragments simultaneously, rather than explicit trials for each.