What is Cloning
What is cloning: It is a method of obtaining several identical organisms by asexual (including vegetative) reproduction. It is the opposite of sexual reproduction: the participation of two individuals of different sex is not necessary. A group of genetically identical organisms or cells is called a clone
What are the types?
There are three different types of cloning:
- Genetic cloning: creates copies of genes.
- Reproductive cloning: creates copies of whole animals
- Therapeutic cloning: creates embryonic stem cells. The researchers hope they can use these cells to grow healthy tissue to replace injured or diseased tissue in the human body.
This process refers to the asexual reproduction of organisms through somatic and sex cells, the population of offspring individuals with identical genotypes formed by asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction refers to reproductive methods without the combination of sex cells or natural asexual reproduction methods.
History of Cloning:
The history of cloning: The first cloning in the animal world was carried out in 1938 German Hans Spemann carries out a series of experiments aimed at removing the nucleus of a cell extracted from a frog embryo and transplanting it into an ovule.
In 1952 Americans Robert Briggs and Thomas King manage to implant the nucleus from the egg of a frog. In 1970 British John Gurdon manages to transplant the nucleus of an adult frog cell to an ovule devoid of its nucleus. These tadpoles failed to reach adulthood.
In 1994 scientists from the University of Wisconsin, clone four calves from cells taken from embryos in an advanced stage of development. Ian Wilmut announces the birth of Dolly the sheep, the first clone of an adult mammal produced from an adult cell extracted from a sheep’s udder in 1997.
American scientists from the Advanced Cell Technology Company in Massachusetts clone a human embryo using methods identical to those that allowed the birth of Dolly in 1999. In 2000 the scientists from the Beaverton Primate Center declared that they had first cloned a rhesus-type monkey, named Tetra.
What is the Process of Cloning and its advantages?
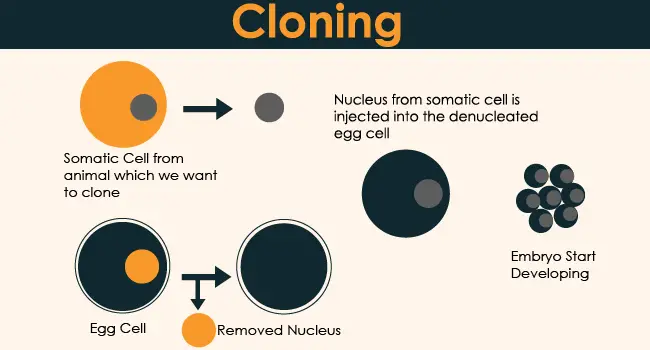
The process of cloning is to first transplant the nucleus of the donor cell containing genetic material into the egg cell with the nucleus removed, use micro-current stimulation to fuse the two, and then promote the new cell to divide and reproduce into an embryo.
After the embryo has developed to a certain degree, it is implanted in the uterus of the female animal to make the animal pregnant so that it can produce animals with the same genes as the cells. If the donor cells are genetically modified, the genes of asexually reproduced animals will undergo the same changes.
Advantages:
The advantages of cloning are as follows:
- Obtaining tissues for transplants without the problems of immune rejection.
- Production of monoclonal antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies are identical proteins that are obtained by this technique the cell that produces this antibody, the B lymphocyte.
- In agriculture: it is possible to grow plants or reproduce animals whose genome is best adapted for large-scale food production.
- Study of hereditary human diseases.
What is cloning used for and why it is important?
The cloning used for:
- Investigation of diseases to obtain possible cures.
- Perform organ transplants.
- In animals, improve the fertility of species and research.
- Improve drug production
Importance:
Why is cloning important: It is important for the study of genetic diseases. It has been a key piece for the study of degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Gene cloning is used to obtain specific genes to generate vaccines, to devise new drugs, and has been studied to improve food quality.
Clone techniques have also had an impact on advances in stem cell cloning to clone organ tissue. It has been of great importance to the advancement of science.