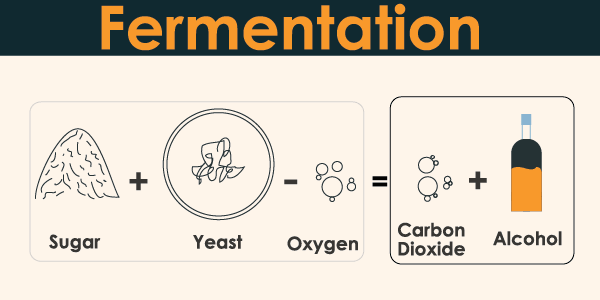
What is Fermentation ?
In this post, I will tell you what is fermentation? It refers to the process of breeding using microorganisms or fungi in a broad sense, and in a narrow sense, a process of sugar decomposition to obtain energy without using oxygen. In many cases, it occurs when carbohydrates decay and proteins decompose.
The process of fermentation and physiological changes carried out by a living body. It is a method of preservation of food through microorganisms. It has traditionally been a way of making food more sustainable. Examples of such products are yogurt, beer and sauerkraut.
Let’s go more in-depth
It is a biochemical reaction that humans were exposed to earlier, and it is now widely used in the food industry, biology, and chemical industry. It is additionally the essential procedure of biological engineering, namely fermentation engineering. It is caused by microbes such as bacteria, mold and yeast.
Fermentations are done by numerous microorganisms, the so-called fermenters, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. This pathway can be straight or branched, in which the oxidation stage lengthens, which is accompanied by an increase in energy yield. It can be carried out in the body of animals, plants and more.
It has two major roles. One is to obtain ATP by oxidatively decomposing organic substances. Another, the reduced NAD is the role to return them to the oxidized form NAD
Let us talk about its types.
Types and Uses of Fermentation:
There are about six Types of Fermentation known. Name of these six types are: Alcoholic Fermentation, Lactic Acid Fermentation, Propionic Acid Fermentation, Butyric Acid Fermentation, Acetic Acid Fermentation, and Methane Fermentation.
- Alcoholic Fermentation: Carried out mainly by yeasts, it produces from certain sugars a quantity of alcohol, ethanol, carbon dioxide, and ATP. This is the procedure used to create alcoholic beverages
- Lactic Acid Fermentation: It consists of partial oxidation of glucose, carried out by lactic acid bacteria or by animal muscle cells. This process generates ATP but byproducts lactic acid, which produces, when accumulated, the painful sensation of muscular fatigue.
- Propionic Acid Fermentation: Acetic acid, carbon dioxide and succinic acid are involved in this process, and propionic acid, a corrosive substance with a pungent odor, is obtained from all of them.
- Butyric Acid Fermentation: It consists in the conversion of glucose in butyric acid and gas, the latter giving it a typically unpleasant odor. It is characteristically carried out by bacteria of the genus Clostridium and requires the presence of lactose.
- Acetic Acid Ferm: Own bacteria of the Acetobacter genus, it transforms ethyl alcohol into acetic acid, that is, alcohol in vinegar. It is, however, an aerobic process, so it can occur in wines exposed to air.
- Methane Ferm: It is one of the metabolic systems of methane bacteria, and is a system that reduces carbon dioxide to methane using electrons such as hydrogen, formic acid, and acetic acid.
I guess you are interested to learn about it
here’s the detail of it.
Uses:
Many human industries take advantage of this to obtain certain substances. In the cheese food industries, propionic fermentation processes are carried out, or in the preservation of many types of foodstuffs, the presence of lactic acid is used, which acts as a preservative, due to lactic acid fermentation.
In the pharmaceutical industry, modern fermentations include the use of bioreactors -fermentors to carry out various medical and health care drugs such as insulin, interferon, growth hormone, antibiotics, and vaccines.
In the chemical industry, it is used to produce amino acids, spices, biopolymers, enzymes, vitamins and single-cell proteins.
Something similar occurs with the alcoholic industry, both for wines, beers or other types of liquors, which require a production process in which alcoholic fermentation intervenes. On the contrary, if some liqueurs like wine are left uncovered for a long time, the added oxygen will start acetic fermentation and the drink will begin to vinegar.