Chondrichthyes vs Osteichthyes , Definition, Differences, Similarities Comparison
Chondrichthyes vs osteichthyes, both are 2 classes of fish divided scientifically.
The number of fish species that have been discovered so far is approximately 34000 around the world which inhabit either salt or freshwater environments.
Generally fishes are cold blooded however Opah which is also called as the kingfish and moonfish is warm blooded. It has different names apart from these two which have been mentioned and these include Cravo and Jerusalem haddock.
also read: habitat and niche differences and comparison
Based on the differences among their endoskeleton, fishes have been divided into two main groups called as Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes.
Differences lie in the composition of their endoskeletons meaning Chondrichthyes have endoskeleton made up of cartilage and Osteichthyes have endoskeleton made up of bones. Chondrichthyes mostly inhabit the marine environments however Osteichthyes can live in both marine and freshwater environment.
What are Chondrichthyes?
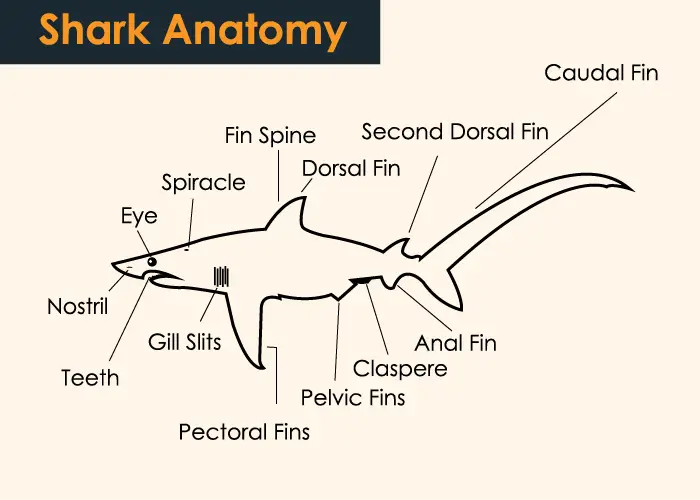
This group of fishes is diverse containing more than 700 known species which are found in marine habitats around the world. It includes sharks, skates and rays. Their skeleton is light and flexible because it is made up of cartilage.
Chondrichthyes body covering is comprised of hard scales titled as placoid scales, such scales are familiarized of protection provision to the organism.
Generally members of the class chondrichthyes have a bony endoskeleton.
The largest member of this group is whale that feeds on plankton and can grow in length up to 60 feet with a weight of 21.5 tons. It can live for 130 years. The main features of this type include 2 chambered heart, tooth like scales, jaws, paired fins and nostrils.
Characteristics of Chondrichthyes
Cass chondrichthyes characteristics are as follow:
- Their body has a tough skin covering with tooth like scales.
- They have mucous glands on their skin.
- They have jaws and paired fins.
- They have 5 to 7 pairs of gills to aid in respiration.
- The male individuals have a reproductive organ which is termed as clasper.
- Chondrichthyes reproduction differs meaning some may be oviparous, viviparous or they may be ovoviviparous.
- They have internal fertilization and development.
- They produce huge yolky eggs.
- Their intestine is small and they have J shaped stomach.
- They have one to two nostrils and they do not open in their mouth cavity.
- Their gonads are usually paired.
- Most of their members can grow up to 21.5 tons like whale shark.
- Chondrichthyes respiration depends on about 5-7 gills, they most often utilize their mouth in order to respire.

Chondrichthyes examples
Examples of chondrichthyes are as follow:
Skates: littles kates, small deepwater skates, Andaman leg skates.
Sharks: whale shark, dogfish, great-white shark.
Rays: electric ray, lesser electric ray, manta-ray, sting-ray.
Chimaeras: Australian-ghost shark, white-spot ghost shark, whitefin shark or whitefin chimaera.
Sawfishes: narrow sawfish, dwarf sawfish
Chondrichthyes Circulatory System
They have a typical closed blood circulatory system that is comprised of a bi-chambered cardiac muscle. In the circulation, blood first travels into the heart chambers, then leaves the heart and travels to gills for processing.
When the blood arrives into gills, it absorbs oxygen from the water that gills are taking in and transport to the whole body.
Define Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes definition: It is the largest class with 28000 known species of fishes. Their cartilage made endoskeleton is replaced with bones once they develop from embryonic to adult stage.
They can be found in marine or in freshwater habitats. The largest member of their group is Mola or Ocean sunfish that grows up to 2300 kg and a length of 2.3 meters. The smallest one is dwarf pygmy goby which only grows to 9 mm to 15 mm in length. This class is divided into 2 groups; ray finned group (single dorsal fin) and lobe finned which have 2 dorsal fins.
General Characteristics
- The shape of their body is round and becomes tapered as it moves to the end.
- They contain gills (4 pairs) which are covered with operculum.
- They have swim bladder (sac like organ) which helps them to swim and maintain balance.
- Their body has lateralis system with sensory organs throughout which is called as neuromast. It helps them to detect vibration and water pressure.
- Osteichthyes reproduction includes the external type of fertilization in which sperm from males and eggs from female combines outside the body after ejaculation and make offsprings.
- The eyes are well developed with nictitating membrane.
- Majority of these fishes are oviparous but some are also ovoviviparous.
- Examples include eels, seahorses etc.
- Osteichthyes digestive system is comprised of a stomach, small intestine, and a spiral valve.
What does osteichthyes mean? It is a fish class that possesses a skeleton also known as made of bone tissues, such fishes also know known as chordates taxonomic phylum superclass.
Osteichthyes Circulatory System
Its circulatory system possesses closed type circulatory system, the whole system is primarily comprised of a gills, heart, blood vessels, and blood itself to flow and supply oxygen.
Gills and RBCs aid in gaseous exchange by bringing in and out fro the body. It also possesses hemoglobin that gives reddish color to RBCs.
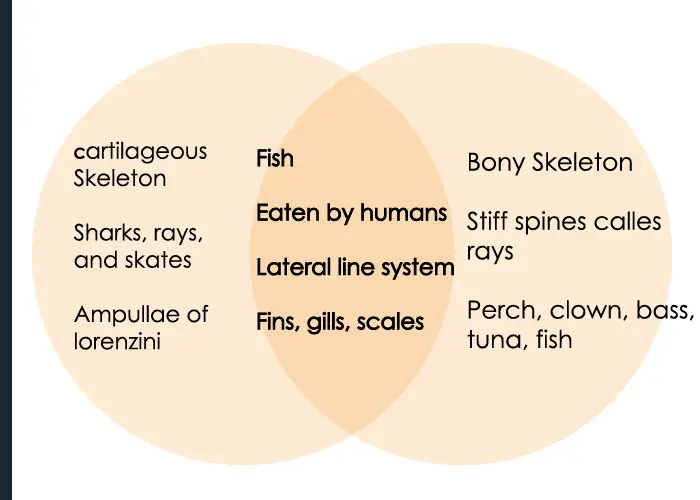
Chondrichthyes vs Osteichthyes Similarities:
- They both belong to the group of aquatic chordates.
- They both come under super class Pisces.
- They both contain exoskeleton as well as endoskeleton.
- They both breathe via gills.
- They both contain mouth with jaws.
- They have paired fins.
| what is the biggest difference between chondrichthyes and osteichthyes? The significant difference among osteichthyes and chondrichthyes is the class, as osteichthyes is cartilaginous fish category having endoskeleton made of bones, while chondrichthyes is having endoskeleton made of cartilage. |
Differences chondrichthyes vs osteichthyes:
| Features | Chondrichthyes | Osteichthyes |
| Common name | Chondrichthyes are also called as cartilaginous fishes because they have an endoskeleton made up of cartilage. | Osteichthyes are also called as the bony fishes because of their endoskeleton containing bones. |
| Habitat | They are found in marine environment however sometimes it happens that some enter they enter the fresh water bodies. | They are present in marine as well as fresh water bodies. |
| Endoskeleton | They contain an endoskeleton made up of cartilage. | They on the other hand contain an endoskeleton which is made up of bones. |
| Types of scales | Their body has a covering of small tooth like scales which are called as placoid scales. | If they have scales present on their body then in that case, scales could be of different types like ganoid and laptoid scales. |
| Size | These are usually large in size. | These are usually smaller in size. |
| Position of mouth | Mouth is located ventrally. | Mouth is located on the anterior side of their body. This kind of mouth is termed as terminal mouth. |
| Gills | These fishes have gill pairs ranging from 5 to 7 in numbers. | These fishes have 4 pair of gills. |
| Operculum | There is no operculum or gill cover present in these fishes. | They have an operculum present on each of their gills for covering. |
| Swim bladder | No swim bladder is present in these. | A swim bladder is present to aid in swimming and to help in maintaining their body balance. |
| Fertilization | Internal fertilization occurs in many of these species. | Majority of the members have external fertilization mechanism. |
| Excretory products | The excretory products of this class include urea. | The excretory products in this class are usually ammonia. |
| Feeding behavior | Normally by nature they are carnivorous. | These have diverse feeding behaviors like some may be carnivorous, herbivorous, omnivorous, detritivorous or might feed by filtering. |
| Examples | Examples include sharks, skates and rays. | Examples include dolphin, salmon, rohu, seahorse etc. |
Conclusion
Fish is a cold blooded organism and has two main groups which are termed as Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes. These groups are distinguished on the basis of endoskeleton present in each. The Chondrichthyes have an endoskeleton which is made up of cartilage however Osteichthyes have an endoskeleton based on bones.
Up till now almost 8.1 percent of the fish species that makes up around 1245 are being listed as vulnerable because of tremendous reduction in their population. Out of these 121 are the cartilaginous fishes however the rest 1114 belongs to the ray finned fish group. The basic reasons behind their vulnerability are exploitation, killing, disease, habitat loss and pollution. It is our duty to provide protection by making strict conservation protocols before they go extinct.