Community Definition Biology, What Does It Mean?
A community definition in biology refers to many individuals belonging to different species. The organisms that make up the biological community (biotic environment) also interface with the non-living environment (abiotic environment). It represented by rocks, water, air, earth, nutrients, organic substances, light.
In ecology, the community is a set of living beings linked together in a certain area, through the food or food chains. It is a specifically interacting, inextricable complex of animal and plant organisms. It depends on the discipline and the perspective from which it is approached.
related: Habitat vs Niche
This is the basic overview of community definition in biology, lets dive bit more in detail.
What are the types and characteristics of the community?
There are two types of community.
Major community: It spans larger geographic areas. It is able to sustain itself and is self-regulating. These are independent over neighboring communities. For example, a lake, a forest, a grassland, and a pond. It is an accumulation of phytocenosis, zoocenosis, and microbiocenosis.
Minor community: make up major communities. It is a smaller unit that is more or less dependent on other accumulation. For example, a collection of organisms, which live inside a slice of deadwood on the woodland floor.
The characteristics of the community are as follows:
• Species diversity.
• Stratification.
• Ecotone.
• Succession.
• Interdependence.
• Periodicity.
• Dominance.
• Trophic Organization.
Importance and example of the community according to biology definition:
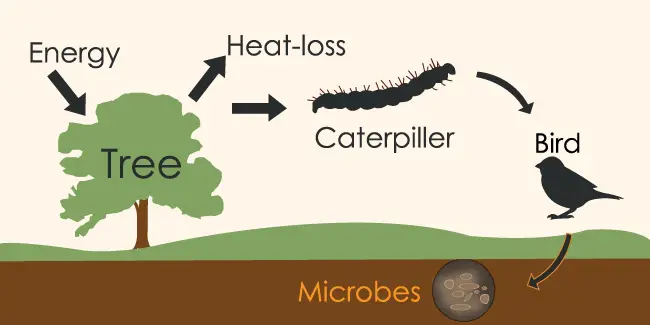
Importance: Community is important because it allows species interaction. All the species feed on each other and depend on each other. For instance, animals are not able to make their own food. Therefore, they depend on other organisms for their nutrition.
On the other hand, plants can make theirs through photosynthesis.
However, Plants also depend on animals. It may also provide a protective shield. For instance, trees provide a habitat for several organisms such as birds, insects, lichens.
Each distinct species of living being makes up a specific population, and their life together makes up the garden community.
You may also enjoy reading: