Microscope With Labeled Parts and Functions
Microscope is a revolutionized scientific instrument which is used in research laboratories to examine the small objects that are not clearly visible and can’t be seen by the naked eye. They are derived from Ancient Greek words “mikrós skopeîn” as mikrós means “small” and skopeîn mean “to look” or “see”.
Microscopes are frequently utilized to research the fungi, microscopic algae,, and other minor life forms. It has its own magnification power and made up of lenses for the magnification. It depends on the type of the lens that it will increase the illustration according to its focal strength. They can see the very small objects and distinct their structural differences, for example the view of the plant and animal cells, viewing of the microscopic bacterial cells.
Microscopes are usually made up of basic parts for holding and supporting the whole body of it and its components and the ocular parts which are used for magnification and viewing of the sampling images.
This Instrument make objects such as cells, microorganisms, viruses, and microorganisms visible to human eye by making larger enough images, so they can be examined and researched.
Types of the Microscope
There are different types of it such as transmission electron microscopes (TEMs), scanning electron microscopes (SEMs), atomic force microscopes (AFM), near-field scanning optical microscopes (MSOM or SNOM, scanning near-field optical microscopy, and scanning tunneling microscopes (STM).
However, the optical for of it is one the most common and famous type.
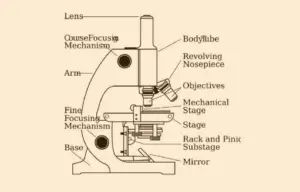
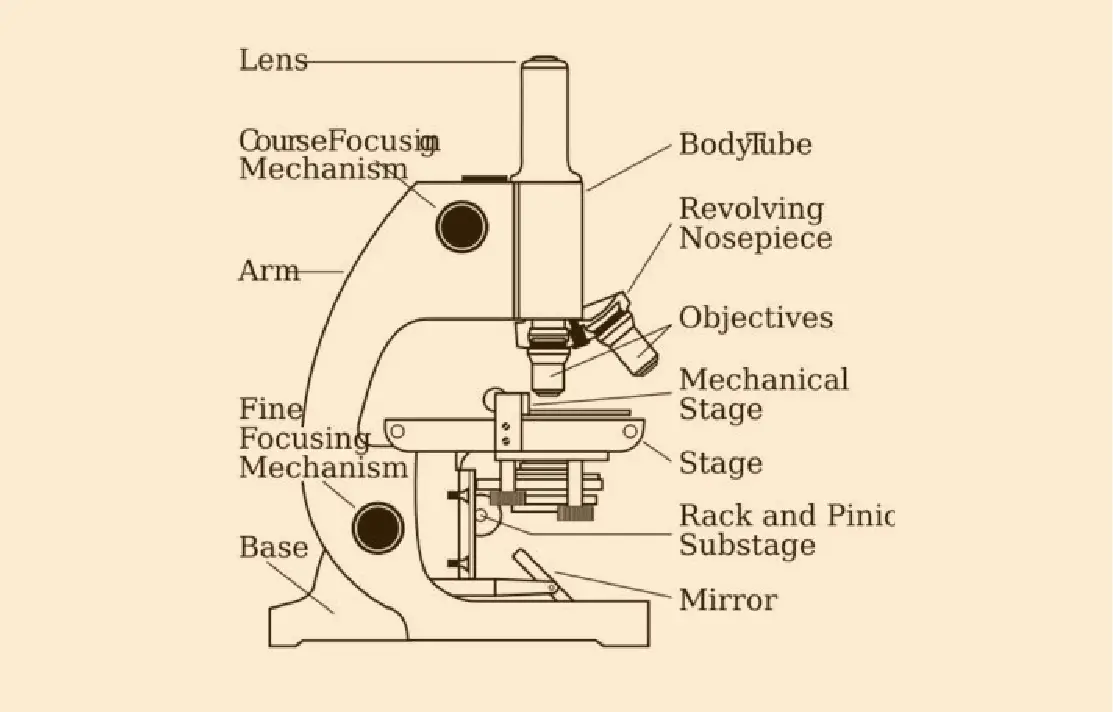
Microscope Parts list
There are three different structural parts of this optical device
- Head
- Base
- Arms
Head
Head is also known as the body of this machine as it brings the optical parts in the upper part of the microscope.
Base
It support the whole apparatus body, and brings the microscopic incandescent light.
Arms
The part that protrudes from the base is used to carry eyepiece stem. It is used to support the head of the microscope and is also used to carry it.
Some high-quality microscopes have a segmented arm with more than one joint. It allowed more movement of the microscopic head for high quality viewing.
Optical parts and the functions
The optical parts of the microscope are used to view, enlarge, and produce an image from a sample placed on a slide. These parts include
Eyepiece:
Eyepiece also contains ocular lens. It enhance the image of the viewer. This part is used for checking through the microscope. Eyepiece is found at the upper part of it. Its standard magnification is 10x with an optional eyepiece and having magnifications from 5X to 30X.
Eyepiece Tube:
It’s the eyepiece holder. It brings the eyepiece directly above the objective lens. Some binoculars have eyepiece tubes that can be easily rotated to achieve maximum magnification. For monocular microscopes, they are none flexible.
Objective Lenses
Three are 3 or 4 objective lenses on a microscope .These are the some main lenses that are used for specimen visualization. They have a magnification power of 40x-100X. There are about 1-4 objectives lenses attached to one microscope, in which some are front-facing and others are opposite-facing. Lenses have differing magnification Capacities.
Nose Piece
A turret is sometimes called a nose piece. It holds the objective lenses. It is movable and it revolve the objective lenses that depends on the magnification power of the lens.
The Adjustment knobs
There are two types of Adjustment knobs, i-e fine adjustment knobs and coarse adjustment knobs. It is used to focus the microscope.
Stage
This is the segment in which the specimen is placed for viewing. The slides are held in place with clips. As the mechanical stage the most common stage, which allows the control of the slides by moving the slides using the mechanical knobs on the stage instead of moving them manually.
Aperture
There is a hole on the stage of the microscopes. The transmitted light reaches through this to stage.
Microscopic illuminator
It is the microscopes light source, located at the base. It is used instead of a mirror. It captures light from an external source of a low voltage of about 100v.
Condenser
These lenses that are used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the specimen.
Diaphragm
It controls the light that passes through the specimen.
Light source
It provides light for viewing the specimen.
Conclusion:
It Include components structurally and optically for the itself, as well as their components, to operate magnification and imaging of specimen images. This describes the portions of a it has and the functions they perform to allow visualization of specimen images.