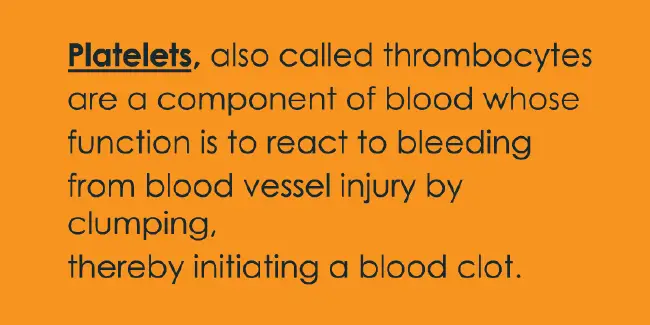
What are Platelets ?
Tiny blood cells that help your body form clots to stop bleeding are called platelets. These are small pieces of cytoplasm that are shed from the cytoplasm of mature megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. They play an important role in coagulation, a very complex phenomenon.

The platelets play a central role in the development of vascular calcification or vascular occlusions such as the heart attack.
Platelet count
Platelet count refers to the platelet number/contained in a unit volume of blood. A normal platelet count range from 140 to 360 thousand / μl blood. The more in number than 450,000 is known as thrombocytosis, while platelets less than 150,000 is known as thrombocytopenia.
When platelets are too high:
An increased platelet count occurs:
- primarily in diseases of the hematopoietic system such as chronic myeloid or polycythemia vera
- after removal of the spleen
- as part of a serious bacterial infection
- after major blood loss in accident/surgery
- during physical exertion and stress
- in diseases of the bone marrow (polycythemia/thrombocythemia)
When platelets are too low:
A reduced platelet count occurs:
- After taking certain medications (e.g. some rheumatic drugs or psychiatric drugs); the platelet count may also drop when using heparin.
- Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
- heavy use of platelets.
- Cancer caused by the displacement of normal bone marrow (e.g. leukemia).
- with alcoholism.
- Blood loss.
- With the enlargement of the spleen; In this case, platelets can be smuggled into the spleen and broken down.
The function of Platelets:
The main function of platelets is to coagulate and stop bleeding, and repair damaged blood vessels. These are important for blood clotting because they stick together in the event of vascular injuries and form a graft at the injured area and become a cause of stop-bleeding.
When the blood vessel is damaged or ruptured, the platelet stimulated, changing from the stationary phase to the functional phase, and immediately deforms.
If there are too few platelets in our blood or if these cells do not function properly, there is an increased tendency to bleed. This means that in the event of an injury, you bleed longer and more. If the platelet function is highly disturbed, bleeding can occur without an external cause (so-called spontaneous bleeding).