What is Alcoholic Fermentation ?
Alcoholic Fermentation is a type of fermentation in which carbohydrates, mainly glucose, are converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide molecules. It is caused by many yeasts and some mold fungi.
It refers to the chemical process in which microorganisms produce alcohol through the fermentation process.
Alcoholic fermentation is also known as fermentation of ethanol or ethylic fermentation. It is generally considered an anaerobic process. It is widely used in alcoholic beverages, fuels, food processing, etc. Certain bacteria, such as Z.mobilis, can also be used for ethanol fermentation.
Alcoholic fermentation is carried out mainly by Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast, which is the common yeast in bread or beer, which converts 90% of the sugar into equimolar amounts of alcohol and CO2. Raw materials are Sucroid substances such as cane sugar, beets, and fruit juices. The main raw material is molasses.
Conditions for alcoholic fermentation:
- Sugar concentration: 10 – 18%
- pH between 4 and 4.5
- Microorganism: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Absence of O2 and the presence of phosphates.
- Fermentation temperature: 15 – 25ºC, above 30ºC the alcohol evaporates.
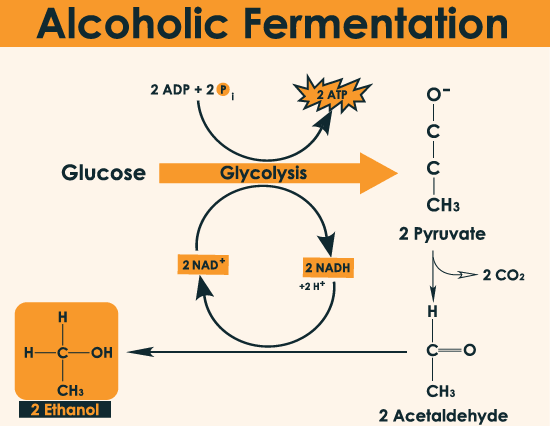
Chemical reaction
The glycolysis pathway is also known as the EMP (Embden-Meyerhof Parnas) pathway. It degrades into a three-carbon compound through a series of steps. An anaerobic glycolysis carried out by organisms to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide from sugar or polysaccharides.
The overall chemical formula for alcohol fermentation is:
C6 H12 O6 + Zymase (enzyme) ~~~> 2C2 H5 OH + 2CO2
First stage: Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and two molecules of NAD and NADH are transformed.
C6 H12 O6 + 2NAD ++ 2pi ~~~> 2CH3 COCOOH + 2NADH + 2H + 2ATP + 2H2O
Second stage: Cracking of sugar, pyruvate is broken down into acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide.
CH3 COCOOH → CH3 CHO + CO2
Third stage: It uses the reducing agent NADH. It is irreversibly inhibited by iodoacetic acid (ICH2COOH) through thiolase catalysis. NAD + is reduced to NADH.
CH3 CHO + NADH + H → C2 H5 OH + NAD
Let’s dig into more knowledge about alcoholic fermentation
Throughout the entire fermentation process, and depending on the conditions (amount of sugar available, temperature, oxygen, etc.), the type of yeast that predominates can be changed, distinguishing several phases in the fermentation:
1st phase (first 24 hours), non-sporogenous yeasts predominate, which resist a 4-5 alcoholic degree. They are sensitive to sulfur dioxide.
2nd phase (2nd-4th day), Saccharomyces cerevisiae predominates, which resists up to an alcohol grade between 8 and 16. This phase is when the maximum fermentation capacity is given
3rd phase Saccharomyces Cerevisiae continues to work together with Saccharomyces Oviformis. There may also be other microorganisms coming mainly from the cellars and utensils, they are usually fungi among which Penicillium, Aspergillus, Oidium,
I guess most of you want to know about the uses of alcoholic fermentation.
Uses of fermentation
Alcohol fermentation has a large number of applications in the alcohol industry, wine industry and food industry. Wine, fruit wine, beer, etc. are all products made by alcohol fermentation. The uses of ethanol in industry are wide and range from the manufacture of cosmetic products, cleaning products, etc.
There is also alcohol fermentation in the process of vegetable pickling, but the alcohol output is low, 0.5% to 0.7%, which has little effect on the main fermentation process in the vegetable pickling process-lactic acid fermentation, but it also plays a role in flavoring Function.
Examples of alcoholic fermentation
This is the process that yields ethyl alcohol or alcohol and its examples can be as follow:
- Production of alcohol in vine organically.
- Production of yogurt/curd lassi.
- Cider production.
These are main food products that are produced as a result of alcoholic fermentation, there are many others.
Fermentation and distillation of alcohol
Fermentation and distillation are two difference processes.
As fermentation is the mechanism of producing alcohol by usage of yeast in the absence of oxygen, while distillation is the mechanism applied on readily fermented products to higher ABV beverages. For instance, distillation appliedbon beer makes whiskey.