What is Nucleic Acid?
What is nucleic acid? It is a large biomolecule usually located in the nucleus, and are the carriers of genetic information. It is long molecular chains made up of the repetition of smaller pieces known as monomers. In this case, they are nucleotide polymers linked by phosphodiester bonds.
Nucleic Acids are the most important biological macromolecules and widely exists in all animal and plant cells and microorganisms. It is one of the most basic substances in life and plays an important role in determining the growth, inheritance, and mutation of organisms.
What is a nucleic acid made of?
What is a nucleic acid made of: The NucleicAcid is made up of molecules called nucleotides. It is built of three elements that have little in common with each other: heterocyclic nitrogenous bases; five-membered sugar of ribose or deoxyribose; phosphoric acid. They are acids due to phosphoric acid residues.
Nucleic Acid types and function:
There are two types of nucleic acid.
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): DNA is a double strand in the form of a helix. It encodes the information the cell needs to make proteins.
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): RNA is single-stranded and linear. It has various molecular forms and is involved in protein synthesis.
Functions
Nucleic acid functions are as follows:
- Expression of the genetic message
- DNA duplication
- Translation, in ribosomes, of the message contained in the mRNA to proteins.
- DNA transcription to form mRNA and others
Structure and example of Nucleic Acid:
Structure of nucleic acid: Each nucleic acid molecule is made up of the repeat of a type of nucleotide. A nucleotide is formed by the attachment of a phosphate group to the 5’carbon of a pentose, which can be deoxyribose or ribose. The nitrogenous bases are cyclic molecules and in the composition of these rings.
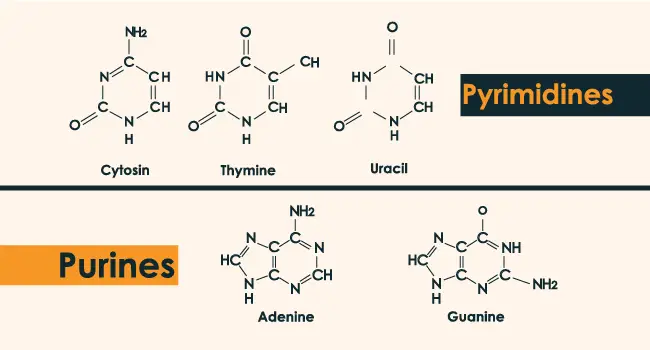
The bases formed by two rings are called puric bases (derived from purine). Within this group, we find Adenine (A), and Guanine (G). If they have a single cycle, they are called pyrimidine bases (derived from pyrimidine), such as Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Uracil (U). These nucleotide bases are the recipe or building blocks of DNA and RNA.
The nitrogenous bases present in DNA and RNA are almost the same, but not the same as it is. DNA possesses Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Adenine but in the case of RNA just the Thymine is replaced by Uracil, this can also be a major difference between them.
A phosphate group, derived from phosphoric acid. The structural composition of each molecule, also, is given in three-dimensional double helix (DNA) or single-chain (RNA) form, although in the case of prokaryotic organisms it is common to find a single-chain circular DNA.
Example:
Nucleic acid examples include Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA), Ribonucleic Acid (RNA). DNA and RNA are natural NucleicAcid. While the acids; Peptide, Blocked Nucleic Acid, Glycolic Nucle Acid, Chemoplasts are synthesized in the laboratory. NucleicAcid located within the nucleus and cytoplasm of cells.
Where is DNA found?
Where is DNA found: if we talk separately about its presence in eukaryotes and prokaryotes then in eukaryotes, it is present in the nucleus but in prokaryotes, as we know there is no nucleus, so it is freely moving in the cytosol of the prokaryotic cell.