
Difference between Virus and Bacteria
The very simple difference between Virus and Bacteria is that Virus is smaller than a bacteria WHILE a Bacteria is larger than a virus. The worthy thing to mention here is that bacteria is considered a fully functional microorganism while a virus lacks characteristics of a fully functional organism.
Organisms are classified into two major categories Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes. Eukaryotes are those organisms having the nucleus in their cells but Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus in their cells. According to biological researches, prokaryotes are classical organisms and came to existence before eukaryote. Bacteria is prokaryote while a virus cannot be yet considered a prokaryote or a eukaryote.
Difference between Virus and Bacteria in the column:
| Virus | Bacteria | |
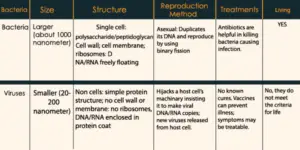
| 1. | It is much smaller than bacteria, and its recorded size is 20-200 nm | It is larger than a virus and its recorded size is nearly 1000 nm. |
| 2. | These are always infectious and are not human friendly. | These are not always infectious there are some bacteria that are human friendly and even help In digestion. |
| 3. | Cannot be considered either prokaryote or eukaryote | There are both eukaryotic and prokaryotic bacteria. |
| 4. | It can even infect bacteria | It cannot infect virus. |
| 5. | It cannot be considered as a parasite. | It can be considered as a parasitic organism. |
| 6. | It always requires a host cell for its replication/reproduction. | It does not always require a host cell for reproduction in fact It can reproduce on their own using the asexual method of reproduction. |
| 7. | Antibiotics cannot kill viruses. | There is a wide range of antibiotics that kills bacteria. |
| 8. | These are very simple in structure with having only DNA or RNA packaged inside a membranous or protein coat. | These have a complex structure including many cell organelles and DNA or RNA inside the nucleus or freely moving without a nucleus. |
| 9. | Illnesses caused by this include Chickenpox, Influenza, Common cold, AIDS, SARS, MERS, Cholera, Plague, Hepatitis, Measles, Ebola, herpes, and rabies. | Illnesses include: Food poisoning, Meningitis, Ear infection, Pneumonia, Strep throat, and gonorrhea |
| 10. | There is no virus in a human body if present then it could be an alarming situation. | There is a large number of bacteria inside the human body to more than the number of humans cells. |
| 11. | Viral infections are always contagious. | Bacterial infections are not always contagious. |