What is Bioinformatics: Career Importance Uses
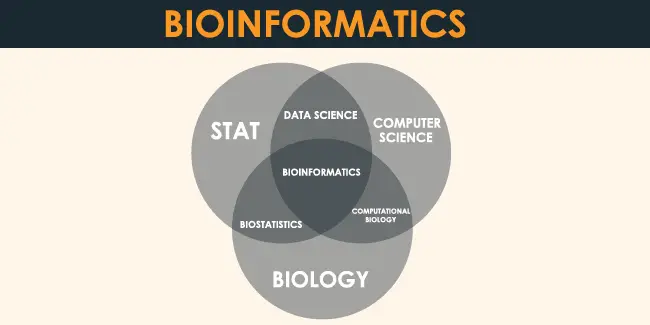
Bioinformatics, an interdisciplinary field that combines molecular biology, genetics, computer science, mathematics, and statistics. It manages and analyzes biological data through computer processing together with knowledge of the area of biology. It applies in biochemistry, biophysics, ecology, and other fields.
Bioinformatics is basically just a combination of molecular biology and information technology. The research materials and results of bioinformatics are a variety of biological data. Its research tool is a computer. It is very useful for the analysis of very small-scale elements, such as proteins and genes.
The purpose of bioinformatics is to serve as a bridge between observations (data) and derived knowledge (information) about, for example, the function of processes and, later, application (knowledge).
Introduction
It has become an important part of many areas of biology. It is in life sciences research into the computer as a tool for biological information for storage, and analysis of science. In the fields of genetics and genomics, it helps in the functional annotation of genomes, detection, and analysis of mutations.
Moreover, bioinformatics helps analyze and catalog the biochemical pathways and networks that are an important part of systems biology. In structural biology, it helps in modeling DNA, RNA, and protein structures, as well as molecular interactions.
Bioinformatics Career
Bioinformatics graduates can anticipate taking part in any weave of research, clinical service, consultation, and teaching. Moreover, many universities, research centers, medical centers, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology companies, also hiring bioinformatics graduates for drug discovery and research on diseases.
It has become an interdisciplinary science, and if you are a biologist, then knowledge in the field of bioinformatics can be of great benefit to you in working with your experiments and research.
Examples:
Examples include:
- data mining
- visualization
- machine learning algorithms
- pattern recognition
- sequence alignment
- assembly of the genome
- gene conclusion
- narcotics detection
- design of drugs
- alignment structure of the protein
- prediction of gene expression
- prediction of protein structure
- protein-protein interactions
- modeling of evolution
- genome association studies
-
cell/mitosis division
Importance
For scientists or bioinformaticists it was the greatest challenge of how to compile and store vast biological data. Except for computers, there was no other solution for the storing of data. So for this purpose, bioinformatics provides opportunities to scientists to store data on computers in the form of a database.
On the other hand, in the field of health and for the study of human diseases, it has very important tools for decision making in the diagnosis, prediction, and treatment.
Furthermore, it is essential for drug designing.
What is bioinformatics used for
Some of the most important applications are:
- Molecular diagnostic
- genetic filters
- genetic improvement of cultures
- findings of new drugs
- therapeutic cloning of germ cells
- reproductive cloning for assisted reproduction
- cloning of genes or pieces of DNA
However, Bioinformatics is one of the branches of modern biotechnology. The latter arises when you begin to study genetic manipulation or genetic engineering.
Structural Bioinformatics
Structural bioinformatics includes the development of algorithms and programs for predicting the spatial structure of proteins.
Research topics in structural bioinformatics:
- Molecular dynamics
- X-ray analysis (XRD) of macromolecules
- Algorithms for finding the hydrophobic core of a protein molecule
- Spatial alignment of protein structures
- Quality indicators of the macromolecule model constructed according to the SAR
- Algorithms for finding structural domains of proteins
- Structural classifications of SCOP and CATH domains
- Macromolecule Surface Algorithms
The biological sciences have advanced in their studies on the origin, evolution, and essential characteristics of living things thanks to the use of computer systems to store, process, and transmit information.
Further, the computer has helped classify a lot of information, creating a database on the correlations identified and unidentified.