
Reptiles vs Amphibians | How are They Different From Each other?
Reptiles vs Amphibians, these are two distinct organism categories that possess backbones and are warm-blooded.
Amphibians are the organisms that have the ability to live dually, as they can live in water and as well as on land. Such animals have moisty porous skin and are cold-blooded animals. Amphibians include crocodile, frog, turtle, salamander, and microsauria etc.
also check: Cytosol vs cytoplasm differences & comparison
Reptiles are the organism type that live out of the water on land. They possess scales on their body and they lay eggs and breathe through lungs.
Cold-blooded organisms are the creatures that can’t control their inner temperature levels as indicated by the necessary level and they continue changing their temperature as per the adjustments in outer environment temperature.
Difference between amphibians and reptiles? amphibians and reptiles are distinct from their relation to the aquatic environment. Amphibians require Aquas habitat as well as dry because they spend atleast half of their lives in aquas environment and they lay eggs there. While reptiles do not spend their lives in Aquas environment, they live solely on land or often near water.
watch an interesting video related to reptiles vs amphibians to get better insights:
Difference Between Amphibian and Reptiles
| Amphibian | Reptiles | |
| 1. | Amphibians are ectothermic or cold-blooded organisms, living on land or in water. They take into consideration their lungs as well as gills for breathing purposes, both in water and land. | Reptiles are likewise one of the cold-blooded or ectothermic creatures, which live ashore, which live on land. They can possess the special reproductive framework as viviparous and oviparous and possess 4 legs. |
| 2. | These animals live in the aquatic environment as well as on land. They spend their adulthood stage on land and larval stage in water. |
They prefer to spend life on land but few of them for instance crocodiles, alligators, and turtles are capable of living in the water. |
| 3. | Toads, Frogs, Salamanders, etc. | Snake, Lizards, Crocodile, etc. |
| 4. | They are oviparous, in which embryos develop inside the mother’s womb in the egg and are hatched outside the mother’s body. | Some species possess viviparous (embryo get flourish inside the womb) on the other hand some possess oviparous reproductive framework. |
| 5. | It includes external type of fertilization | It includes internal fertilization. |
| 6. | Amphibians can breathe in both ways, which can be through gills or from the lungs. | Reptiles breathe only through lungs. |
| 7. | They have the restriction of visualising certain colours, which means they have the restriction to narrow bands of the colour spectrum. | They possess the capability to distinguish or visualize a wide color range. |
| 8. | Amphibians have a three-chambered heart. | Reptiles possess tri-Chambered cardiac muscle with ventricle divided through a spectrum ahead. |
| 9. | Amphibians secrets toxins from their skin, which protect them from predators. | They possess protective tough scales all around their skin. They also capable of utilizing nails and teeth manufacturing toxins. |
| 10. | Smooth, sticky, moist and highly porous skin to perform the various function. | they possess tough and dried skin that aids in their protection. |
| 11. | Amphibians lay their eggs in water which are covered with gel. | They lay eggs on land with hard calcified covering. |
| 12. | They have webbed feet, which help them in swimming and jumping. | they possess tetra limb sets that assist them in swimming, climbing, and running. |
Also read: autotrophs vs heterotrophs difference comparison guide
Definition Amphibians vs Reptiles
Reptiles:
Reptiles are multicellular eukaryotic ectothermic land-living vertebrates. They are capable of laying eggs on land and possess lungs to respire. Snakes, dragons, lizards, turtles, and crocodiles are the best instances of them.
they own another crucial skin-related characteristic which is tough, scaly, and protein-rich to shelter them. This feature allows them to live in a saline environment.
They lay eggs in a burrow incubate them using their body heat and produce alike offsprings.
Amphibians:
Amphibians are also known as dual livers. As they are capable of living inside the aquas environment as well as dry land environment. These are also multicellular eukaryotic ectothermic organisms that are capable of adjusting their internal temperature levels according to external environment.
They own porous soft skin filled with lipid bi-layer. They are also known as cold-blooded animals. They breed underwater and their offsprings get to their mature stage inside water. They most often spend their children life inside the water, and after they get mature then they spend the rest outside on dry land.

Features list of Reptiles vs Amphibians.
Reptiles:
- They shed scales on their skin in contrast to skin cast.
- They possess their body divided into trunk trail and neck.
- Possess rough & dried skin with the absence of glands in the skin layer.
- Are cold-blooded creatures that are found mostly in warmer regions of the earth.
- They respire utilizing their lung framework.
- Their skull is monocodylic in nature.
- The more commonly possess tri-chambered cardiac muscle.
- the lateral line framework is not present.
- 12 couple cranial nerve together make the nervous system.
- They are grubbing & terrifying creatures possessing a scaly body.
- They are ammonotelic, ureotelic, and uricotelic.
- They consider the internal mode of fertilization and their eggs are extremely yolky.
- They are familiarized with possessing moralistic segmentation and a typical cloaca.
- Turtles, snakes, lizards, and crocodiles are a few instances.
There are many features from the features listed above that are not present in the snakes as snakes are a reptile category.
Amphibians:
- They usually possess coupled fins.
- They possess smooth and sometimes rough nonscaly skin with glands embedded in the skin layer.
- They may possess tail or may not, and their body is usually partitioned into trunk & tail.
- They perform locomotion using their bi-paired limbs.
- They consider cutaneous respiration (respiration includes skin and lungs).
- They own tri-chambered cardiac muscle.
- They possess cranial nerves with 10 pairs.
- While their development phase lateral line is available.
- They develop indirectly along with metamorphosis.
- They possess discrete genders with the external mode of fertilization.
- They are ectotherms that are found mostly in warmer regions.
- They are capable of living in water as well as on dry land.
- They secret urea and ammonia as excretory material. Also, they possess mesonephric kidneys.
- Males do not possess penis/copulatory organ.
- They breed underwater.
- Salamanders, frogs, Gymnophiona, caecilians, microsauria, and amphiuma are few amphibians instances.
Reptiles vs Amphibians Reproduction System.
Both reptiles and amphibians reproduce sexually, but the distinction relies on the type of sexual reproduction. reptiles consider internal while amphibians consider external (especially for frogs) types of fertilization.
Males reptiles possess more than one copulatory organ that discharges sperm shot into the female cloaca. So the fertilization process starts inside the female cloaca and ultimately the fully fertilized egg comes out of the cloaca opening from the female body.
Amphibians consider external fertilization most commonly in frogs, they usually lay huge quantities of eggs all at once, and they frequently do as such in gatherings, all storing their eggs in a similar spot simultaneously.
Similarities between reptiles and amphibians
Both are capable of regulating their internal body temperature according to the external environment, due to this feature they are AKA ectotherms.
Both utilize the sexual mode of reproduction.
Both are vertebrates and possess a backbone.
Both are usually found omnivores.
They utilize skin adaptation in cover for thermoregulation in protection purposes keeping the internal heat levels maintained.
Both are multicellular eukaryotic organisms.
Both are cold-blooded animals.
Reptiles vs Amphibians Venn Diagram
The following reptiles vs amphibians Venn diagram represent a quick overview of differences and commonalities between these two terminologies.
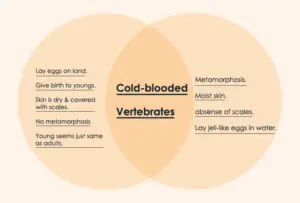
Conclusion:
In the above article, we have gone through two distinct animal categories having different lifestyles on the earth. Both are different animals categories but somehow similar to each other at some points. The above article is a basic overview of the reptiles vs amphibians differences and comparison.