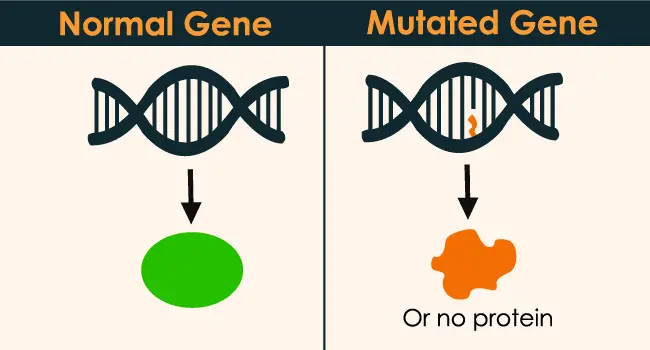
What is Gene Mutation?
Gene Mutation is a persistent deviation/change in the DNA sequence that forms a gene. Such mutations can affect from one structural element of DNA to a large segment of a chromosome containing a number of genes. It may mean that the cell does not produce the protein the body needs.
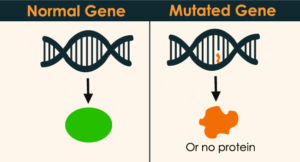
Genetic mutations are changes that occur in a human genotype. A genotype is a human’s genetic information, which is contained in each person’s DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid. This means that DNA contains all the human genetic material. When this DNA is mutated or the original phenotype is changed, malicious or unknown proteins are synthesized which could be an alarming situation for the body.
In various animals and plants including humans, when exposed to carcinogens and mutagens, high-frequency abnormalities in gene DNA (deletion or substitution of DNA bases) occur in cells. When gene mutation occurs in somatic cells, cell death and canceration occur at the individual level.
Causes of gene mutation:
Genetic abnormalities may occur naturally or may be caused by a mutagenic source depending on the environment. Mutagenesis sources include radiation such as X-rays or gamma rays, ultraviolet light, cigarette smoke, and dioxin. It is also said that it is more likely to occur with aging.
Gene mutation cancer:
Gene mutations that cause cancer/uncontrolled cell growth can be caused in two different ways. It can gradually form over several years, leading to “sporadic” cancers; mutations can also be obtained through inheritance, and genetically abnormally functioning genes can cause family hereditary cancers.
Types of cancers caused by mutation:
- Colon cancer: Defects in DNA repair genes (such as MSH2) make patients more likely to develop hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer ( HNPCC ).
- Breast cancer: BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes that are mutated through inheritance are known risk factors for breast cancer. Although many (if not most) breast cancer patients do not detect mutations in these two genes, having such mutations increases the likelihood of breast cancer.
- Eye cancer: Rb tumor suppressor genes ( tumor Suppressor defect) can cause eye cancer and several other types of cancer.
Here’s more detail about it
Types and examples of Gene mutation:
Types of gene mutation are as follows:
- Substitution mutation: Substitution mutations are exchanges of nitrogenous bases with others. This occurs when the mechanism fails during the cloning process and the DNA strand is misplaced. It is not harmful unless codons are formed or amino acids from the protein’s active center are affected.
- Insertion mutation: Insertion mutation occurs when extra bases are added. And as a result, individuals can suffer from several diseases. Reduction of whiteness or melanin pigmentation in the eyes, skin, and hair. Tyrosine cannot be synthesized from phenylketonuria or phenylalanine in the liver.
- Deletion mutations: In deletion mutation, the base is removed. Insertions and deletions are more severe than substitutions because they change the entire amino acid chain. So, as a result, the message that the DNA needs to transmit is encoded incorrectly.
- Translocation mutation: This mutation changes the position of the DNA segment. The fragments of the molecule are broken and bound to other places. This translocation causes the emergence of new nitrogenous base triplets. It causes the message to be encoded incorrectly, such as in deletion or insertion mutations.
The effects of base mutations on the amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain are generally of the following types.
- Synonymous mutation: After the base substitution, while each codon into another codon, but because of codon degeneracy, thereby changing the former, the amino acid encoded by the codon change, Therefore, the mutation effect does not occur. It accounts for approximately 25% of the base substitution mutations.
- Missense mutation: The substitution of base pairs turns a certain codon of mRNA into a codon encoding another amino acid is called a missense mutation. It can cause abnormalities in the structure and function of certain proteins or enzymes in the body, which can cause disease.
- Nonsense mutation: A password encoded amino acid is mutated to a termination codon, early termination of the polypeptide chain synthesis, To produce polypeptide fragments with no biological activity, called nonsense mutations. In most cases, this mutation will affect the function of the protein or enzyme.
- Stop code mutation: Also known as ‘terminator codon mutation’ is a mutation in a gene where a termination code is mutated into a codon encoding an amino acid. For example, the human hemoglobin alpha chain mutant Hb Constant Spring has 31 amino acids more than the normal human alpha-globin chain.
Here are the examples of gene mutation:
- Sickle cell anemia
- Cystic fibrosis
- phenylketonuria
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Color-blindness
- Cancer
You may also enjoy reading :
- definition of homozygous
- what is an allele
- what are chylomicrons
- what is Northern Blotting
- what is gene therapy
- what is cloning
- what is human genome project
- what are stem cells
- what t is vaccine
- what is nested PCR
- what is gel electrophoresis
- what is multiplex PCR
- what is alcoholic fermentation
- what is fermentation
- what is polymerase chain reaction