Carpel and Pistil Definition, Differences, & Comparison
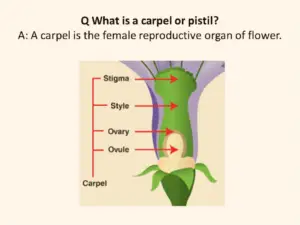
Carpel and Pistil both are generative parts of the plant in flower, and they possess a very small distinction among them. As carpel is made of ovary, stigma, and style, while pistil is the combination of the carpels or it can be a sole carpel, so that pistil exists due to the fusion of many carpels.
check: Difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs
One can undoubtedly recognize the number of carpels by checking the quantity of styles. Interestingly, the quantity of pistils can be recognized by the presence of the quantity of ovaries in bloom.
The blossom expresses to the angiosperms group of a plant, and they are the conceptive structure. A total blossom has unmistakable regenerative structures and in indicated shading and structure. Along these lines, a bloom has four whorls, the lower whorls, and the upper whorls.
The two upper whorls are referred to as conceptive whorl as they participate in multiplication. Further, these whorls are composed of microsporophylls and megasporophylls, where microsporophylls are titled as stamens and megasporophylls are named as carpels (angiosperms).
The lower two whorls are referred to as extra whorls as they legitimately don’t take an interest in the generation of the bloom.
The third whorl is the male whorl and named as androecium, while the fourth whorl is the female part and known as gynoecium. The function of the extra pistil is to ensure the basic organs, and essentially it pulls in the pollinating pests.
The anthology is the field of science that manages the investigation of blooming plants and blossoms and different properties of Angiosperms. With this, we will consider the basic contrasts between the two primary pieces of the bloom, which are carpel and pistil, with a short depiction of them.
Difference Between Pistil and Carpel
| Carpel | Pistil | |
| 1. | Carpels are the female conceptive aspect of a rose that might be available independently or in a few. | Pistils are the female aspect of a blossom bearing seed or ovule. |
| 2. | Carpel manufacture egg cells | They do not produce egg cells. |
| 3. | It is made with the combination of units of ovary, stigma, and style. | It is made of numerous carpels or sometimes one. |
| 4. | Carpels go through the process of fertilization. | It does not go through the fertilization process. |
| 5. | Assist in seed production and its dispersal. | Does not assist in seed production and though employed as a female flower part. |
What are flower?
Flowers are considered the regenerative aspect of a plant, which comprises of sepals, petals, stamens and pistils. A total bloom comprises of both vegetative and regenerative parts, which assume a significant function during the time spent proliferation in plants. Among all other conceptive parts, carpels and pistils are the essential units of the gynoecium-the female aspect of a bloom.
Which part of the flower becomes the seed? The ovule is that flower part that becomes the seed. The ovary is the flower section that transforms into fruit and the ovule following fertilization transforms into seed.
Where are the ovules stored? Ovules are also known as eggs are enclosed in the ovary of the flower before they get into the fertilized state.
What is Carpel?
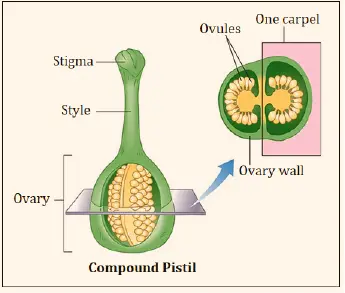
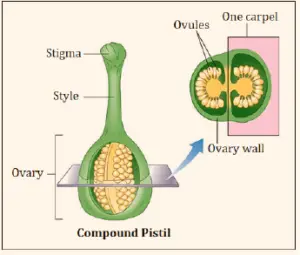
The carpel biology definition states that it is the most profound whorl that exists in the rose, and it is the megasporophyll and seed-bearing, adjusted leaflike structure bearing ovule. Carpel flower or simply a carpel is composed of the ovary, style, and shame. It is the conceptive aspect of a blossom.
The seed advancement inside the carpel plants happens, when the dust grains from another bloom enter and treat the egg inside the carpel.
Carpel function
It is the female regenerative/reproductive section of the plant that gives a high point to the ovary which is a basic ovule container that later on transforms into seeds to the ovary and ultimately to a fully grown fruit.
What is Pistil?
The combination or the association of at least one carpels make up the pistil. It is the female aspect of the bloom, that is midway found and has a swollen base, the ovary that has ovules or likely seeds, it likewise has a style or a tail, rising up out of the ovary, the shame (the tip for accepting dusts) that can be of different shape and is very clingy.
At the hour of fertilization, appropriate dust grains fall on the stigma, that sprout by shaping dust tube. By becoming down through the style, the dust tubes move the sperm for preparation of the ovules in the ovary.
The pistil is shaped by the various leaflike structure enlisted inside one another or of the carpels, that have at least one encased ovules. The carpel is the seed-bearing changed leaf, and there can be one carpel, at least two carpels (compound pistil) if the carpel is at least two in numbers in a pistil and joined together thus known as syncarpous, while if the carpels are isolated in blossom so-known as apocarpous.
Pistil function
The very key pistil function is to work as a manufacturer of ovules, some other purposes include to work as a colleen part of the blossom and aids in fertilization after getting pollens.
Similarities between Carpel and Pistil:
- Their job is to create seeds, go through treatment, helping in seed dispersal and delivering eggs.
- Both carpel and pistils are the female aspects of bloom or flower.
- Seldom both are formed of ovary, stigma, and style.
Where are the male gametes are found in a flower? Male gametes are stores with pollen grains. If we talk about their manufacturing site, then both female & male gametes are manufactured in the ovule and anther
Some Important differences to remember between carpel and pistil:
- Carpels manufacture egg cells, while, in the pistil, there is no egg cell creation.
- Carpels uphold in the creation of seed and its dispersal, in spite of the fact that pistil doesn’t deliver seed, and however fill in as a female aspect of the bloom.
- Carpels are made out of Stigma, ovary, and style, and pistils are the association of one or various carpels.
What a pistil with many carpels is called? A pistil with many carpels is known as gynoecium. If a gynoecium possesses sole carpel, it is known as monocarpous on the offside, if it possess many carpels then it is known as syncarpous
Conclusion:
Flowers are the most fundamental and unique characteristic that exist in the angiosperms. Flowers has several other sections also, which make it a whole one and these include: Ovary, stigma, pistill, stamen, anther, petal, receptacle, sepal, and peduncle.
Carpel vs pistil, both are interchangeable words when there are just a single carpel and one pistil in bloom. As both are the aspects of the female regenerative framework. Indeed, even these have some normal parts likewise that assume a basic function in the bloom fertilization.